Companies everywhere are handling more data than ever and all these terabytes of data need to be stored somewhere. Should you store the data in a database, a data warehouse, or a data lake? How do you know what is best for your company?
Choosing the right data storage solution will depend greatly on how the data is going to be used. While both a data lake and a data warehouse share the goal of the process data queries to facilitate analytics, their functions are different. This post will give you an overview and use cases to understand when to use a data lake or a data warehouse.
What is Data Lake?
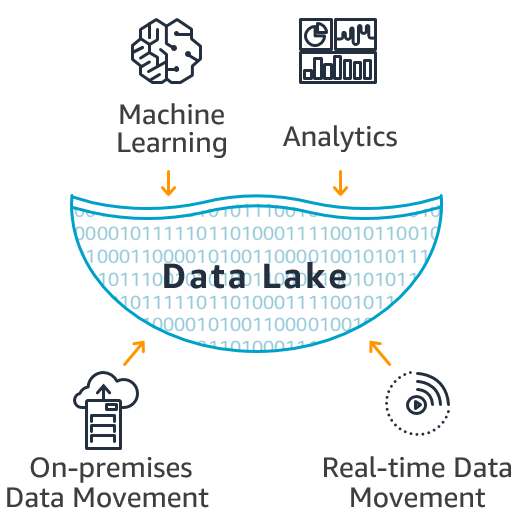
A data lake is a repository that holds raw data, of which the purpose is not yet defined or requires a very high level of flexibility and agility. A data lake allows you to store all data, at its raw format, structured and unstructured in a central repository. You can store the data without having to structure it first.
The data lake may not use databases to store the data, using flat files or logs instead.
Use Cases
A data lake is a good choice when you need to store a large number of records without knowing if you will need them in the future. Data lakes work great to store historical data and support compliance. One of the most common use cases is storing data coming from IoT sources for near-real-time analysis. Here are some examples:
Healthcare: Data lakes help healthcare organizations comply with regulations related to data, medical records storage, and privacy. The lake allows them to store patient records and retrieve data for queries years later. These types of services for healthcare companies usually only store and retrieve data without analyzing it.
Network Security: These types of companies collect raw data through different endpoint devices, like routers and IoT sensors. The large numbers of data need to be stored somewhere in case someone wants to check an anomaly. Typically, the data is stored in the data lake for a few weeks. If there is no need to analyze it, the system destroys the data.
Pharmaceuticals: These organizations collect raw data when they conduct drug trials. They also report for regulation. In this case, organizations retain the data for a long time to help future research.
Querying a Data Lake
You need to take into account that you are querying raw data coming from disparate sources. This can make the process a bit challenging. To simplify this process, you can query the data lake using an Athena query. Amazon Athena is an interactive query service that allows analyzing data in a data lake in an easier way by using standard SQL.
The ability to handle all types of data makes data lakes very attractive for businesses. Industries from oil and gas, marketing, and smart city initiatives.
What is Data Warehouse?
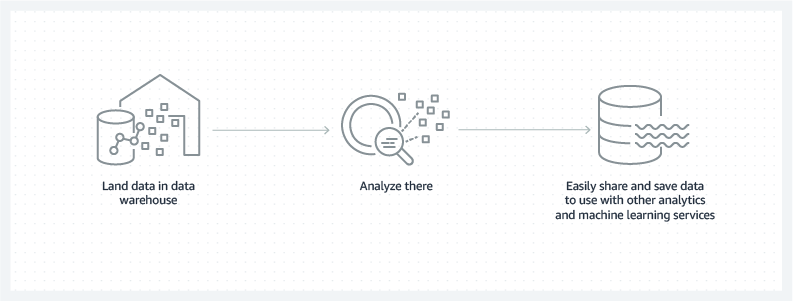
A data warehouse is a repository of processed and structured data with a defined purpose. Some may define a data warehouse as a collection of databases since it receives data from relational databases and transactional systems.
Typically, a data warehouse stores optimized data. That’s why data warehouses are specifically designed for interactive data analytics.
Use Cases
Every industry that uses structured and unstructured data for analytical reporting and business intelligence, can benefit from a data warehouse. Let’s see some examples:
Banking and Finance: Financial institutions use the analytic powers of a data warehouse to identify risks and analyze products. They also can track the performance of accounts and services and interchange rates.
Government: A data warehouse can keep official records (tax, criminal, health policies). It can help government agencies to detect patterns and identify criminal activities, including threat and fraud detection.
Manufacturing: Data warehouses help simplify the supply chain and operations by allowing them to easily retrieve and compare data. For example, comparing sales and performance over regions.
Data Lake vs Data Warehouse
| Data Lake | Data Warehouse | |
| Data Structure | Raw data | Modeled / optimized data |
| Purpose of Data | Flexible | Defined |
| Easy to update | Quick to update. Easy to access and change. | Updates take more effort. More structured by design makes it more difficult to manipulate. |
Wrap Up
While data lakes and data warehouses serve different purposes, some companies may need both. They’ll need to use a data lake to store raw and unstructured information, and a data warehouse to store structured data, analytics, and aggregated reports.
Ultimately, the choice of using one or another will depend on your company’s needs. That being said, the data lake vs data warehouse discussion just started, and choosing the right model (or both) for your company can be critical for growth and efficiency.
